In the life cycle of consumer products, there are usually two situations that will be impacted. One is bump and bounce caused by vehicles on bumpy roads during transportation, and the other is product impacted by falling to the ground, when user moves around. For portable products (such as mobile phones, tablet, wearable devices, etc.) , when they are not protected by cushioning materials, the impact of the drop will cause direct and stressful damage to the product. For electronic products installed on the vehicle, it is even more important, since the environment is harsher than general commercial application; especially the product is installed in tires, doors, or trunks and structural strength must be higher. Therefore, during the product design stage, the Shock Fragility Test can be used to quickly verify the structural strength level and determine whether the packaging cushioning design is appropriate.
The following stress is normally used for Damage Boundary Curve validation:
- Product’s Critical Velocity (ΔVc)
- Product's critical Acceleration (ΔAc)
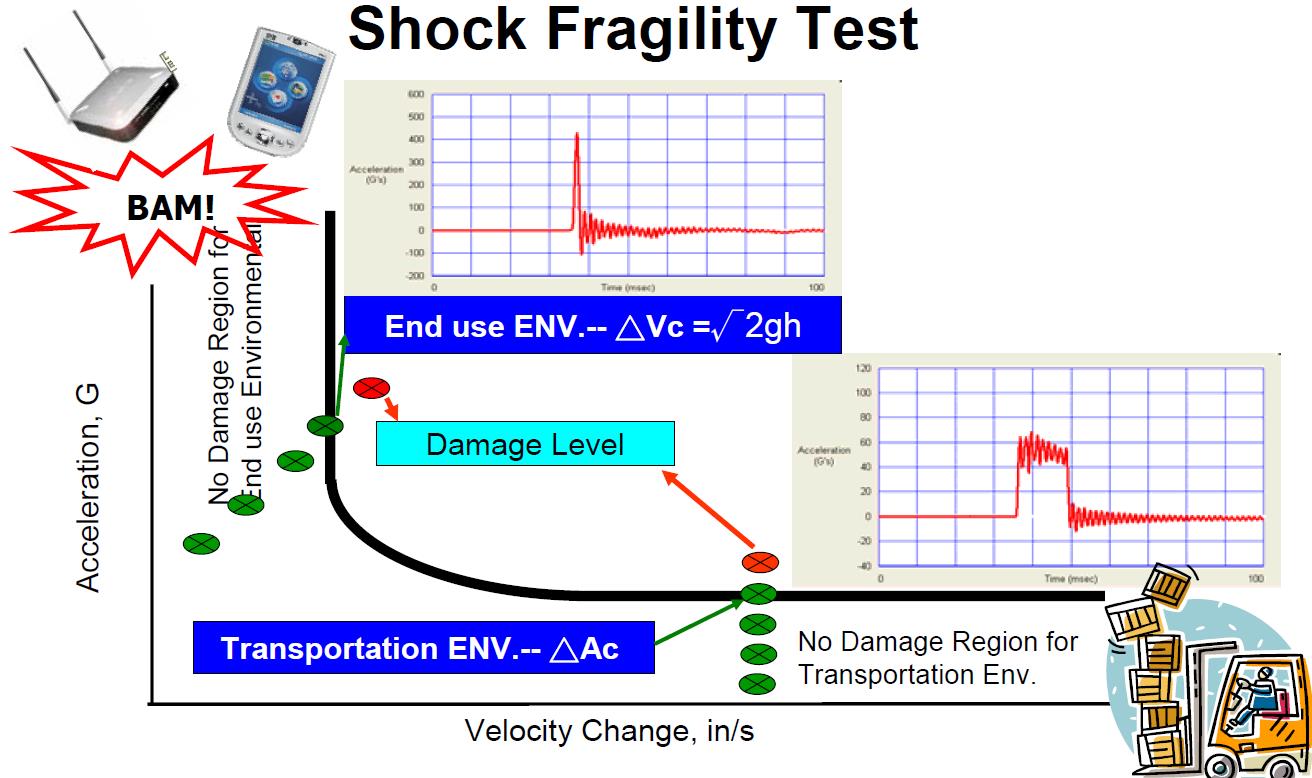
<Damage Boundary Curve Concept>
Ref. standards: ASTM D3332, DELL Packaging Test Plan, HP Testing Procedure.

To make all your PROBLEMS SOLVED, we provide professional consultant and service.
For more information or service, please feel free to email to 📧 sos@dekra-ist.com




